
However, protozoa differ from prokaryotes in having mitochondria that have to be duplicated and divided as well. In protozoan fission, the process is similar as it entails similar fundamental stages. Another group of organisms that reproduce by binary fission is the protozoa. As already mentioned above, bacterial fission entails chromosomal replication, chromosomal segregation, and cell splitting. Bacteria, for instance, use it as a way to reproduce. Several organisms perform binary fission. Product: two cells with an identical genome Stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase Stages: chromosome duplication, chromosome segregation, cytokinesis Mitosisįunction: cell growth (in numbers) in multicellular organisms They will become a somatic cell that will either develop into a specialized differentiated cell or a cell that divides mitotically to give rise to another set of new cells. The new cells from mitosis will not be a new individual as it is in binary fission. The spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes to move and divide the chromosomes into two equal sets at opposite poles. Furthermore, spindle fibers are one of the features that define mitosis. The genetic material is replicated prior to mitosis whereas this stage occurs as part of binary fission. While binary fission is for reproductive purposes mitosis is primarily for growth in multicellular organisms. Differences Between Binary Fission and Mitosisīinary fission is similar to mitosis in the way that the process ultimately leads to the production of two identical daughter cells. In oblique binary fission, cell division occurs obliquely, which may either by left or right oblique. In longitudinal binary fission, the cell divides longitudinally. (5) Septum forms in the middle of the cell. The figure shows how bacteria reproduce through binary fission. Inside a bacterial cell, the stages are as follows: (1) genomic replication, (2) chromosome segregation, and (3) cytokinesis.
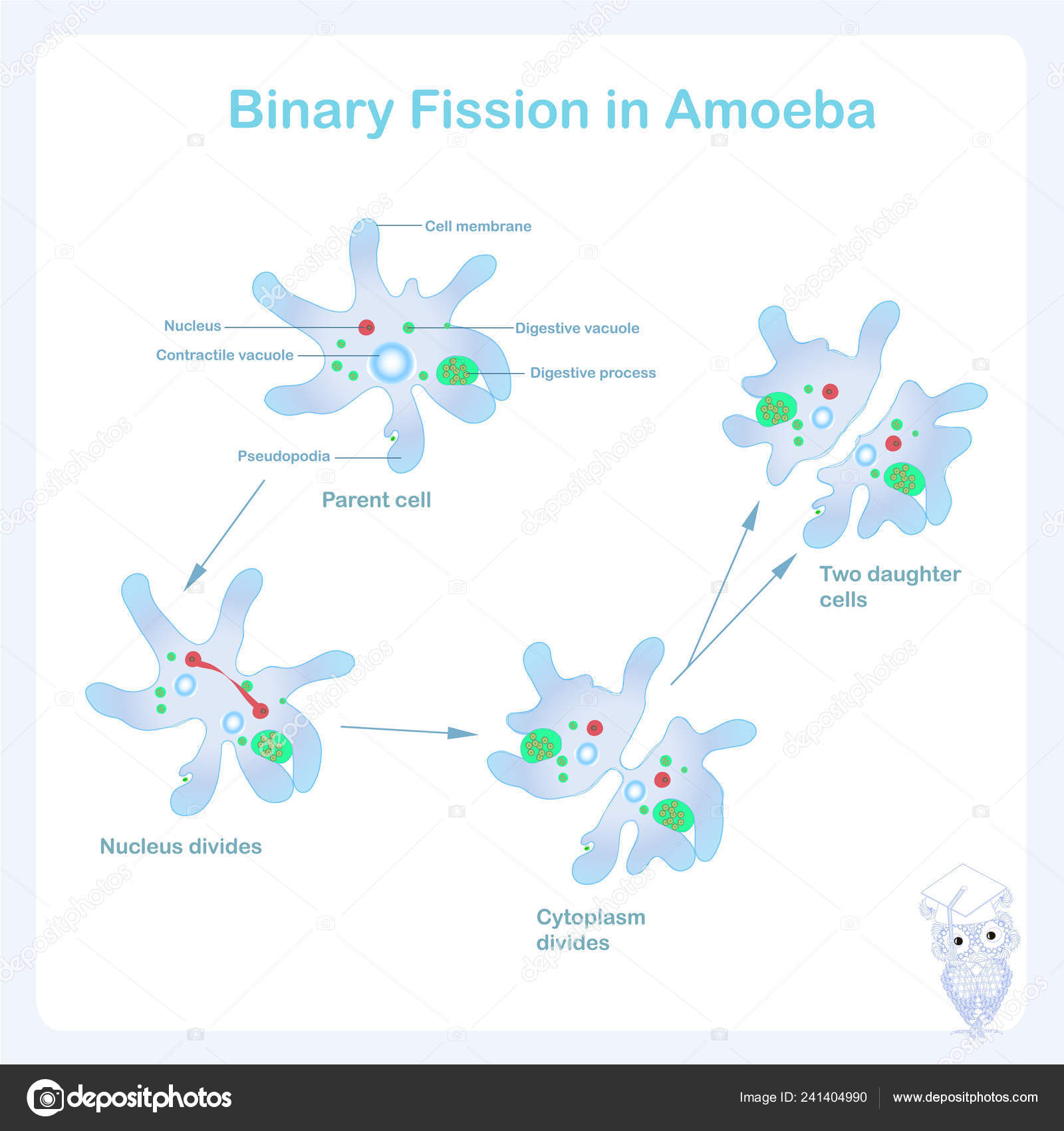
As shown, the method of bacterial replication appears to be fast and simple. Below is a diagram depicting a bacterium undergoing cell fission. The new cell wall often starts out as a “Z-ring” as formed by the cytoskeleton FtsZ. A cell wall also forms if the original (parent) cell has one. The cytoplasm is subsequently cleaved into two by a new cell membrane forming ( cytokinesis). Next, the chromosomes segregate to separate poles of the cell - a process called “karyokinesis”. The process starts by creating a replicate of the genetic material. The prokaryotic cell contains DNA that is tightly coiled prior to cellular splitting. in cyanobacterium Stanieria) 1, the result is an offspring that has the same genome as the parent. Similar to other modes of asexual reproduction, such as budding and formation of baeocytes (e.g. How does binary fission work? Binary fission is the way that prokaryotic cells and certain protozoans reproduce. archaea, eubacteria, cyanobacteria, and certain protozoans (e.g. Binary fission is common among prokaryotes, e.g.

The offspring is a clone because its genome will be identical to that of the parent. Instead, the somatic cells undergo an asexual process that will produce a clone of the parent. The word asexual describes a reproduction that occurs without involving sex cells (gametes). What is binary fission? In biology, binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a parent cell divides, resulting in two identical cells, each having the potential to grow to the size of the original cell. Differences Between Binary Fission and Mitosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
